CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 1

CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 1
Q. 1 Match the animal in Column X with its characteristic in Column Y.
| Column X | Column Y |
|---|---|
| A. Snakes | I. Lateral line |
| B. Spiders | II. Heat sensing pits |
| C. Fishes | III. Echolocation |
| D. Dolphins | IV. Spinnerets |
Which one of the following options represents all correct matches between Column X and Column Y?
- A-II B-IV C-I D-III
- A-I B-II C-III D-IV
- A-Ill B-I C-II D-IV
- A-II B-III C-IV D-I
Answer : 1
Explanation:
- Snakes (A-II): Possess heat-sensing pits (especially pit vipers) to detect warm-blooded prey.
- Spiders (B-IV): Use spinnerets to produce silk.
- Fishes (C-I): Use the lateral line system to detect water movements.
- Dolphins (D-III): Use echolocation for navigation and hunting.
Q. 2 Which one of the following statements is NOT part of the neutral paradigm in ecology?
- All individuals in the community have equal fitness and competitive ability.
- Loss of competing species to extinction is through a slow, random process.
- Diversity is maintained by speciation rates counteracting extinction rates.
- Ecological drift results in stable coexistence of a given set of species.
Answer : 4
Explanation:
Neutral theory assumes that species are ecologically equivalent, and biodiversity is shaped by random processes (ecological drift, speciation, extinction).
- Ecological drift does not lead to stable coexistence; instead, it may lead to random loss of species.
Q. 3 An enzyme has been found to efficiently catalyse the following reaction:

Which one of the following parameters will be increased over the uncatalyzed reaction by the enzyme?
- kr
- Keq
- 1 /kr
- 1/Keq
Answer : 1
Explanation:
Enzymes lower the activation energy, thereby increasing the rate constant (kr) of the reaction.
- Equilibrium constant (Keq) is determined by ΔG°, not affected by enzymes.
- Enzymes do not change Keq, 1/kr, or 1/Keq.
Only kr increases in catalyzed reactions.
Q. 4 The figure below depicts the feedback regulation in the biosynthesis pathway of three branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) – Leu, Val, and Ile, acting at three major steps catalyzed by enzymes AHAS, IPMS, and TD. The activity of AHAS is feedback regulated by the synergistic combination of Leu and Val. lPMS activity is regulated exclusively by Leu. Ile regulates TD activity while Val can relax this feedback regulation on TD by Ile.
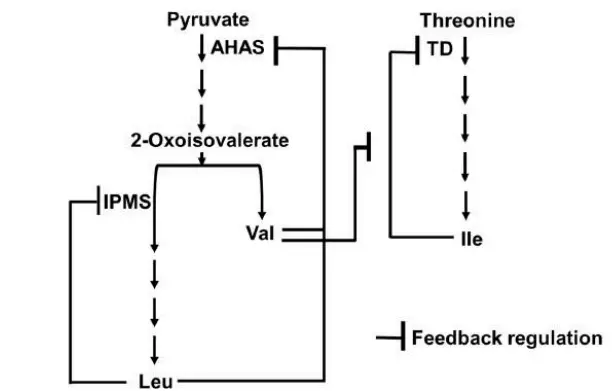
Which one of the following possibilities of BCAA pools is likely to occur in the RNAi knockdown of IPMS?
- Both Leu and Val will decrease.
- Leu will decrease, and Val remains unchanged.
- Leu will decrease and both Val and Ile will increase.
- Only Leu will decrease.
Answer : 3
Explanation:
- IPMS is essential for Leu synthesis and is inhibited by Leu.
- When IPMS is knocked down, Leu levels drop.
- Low Leu removes inhibition on:
- AHAS → increasing Val and Ile synthesis.
- TD → boosting Ile production.
- As a result:
- Leu ↓
- Val ↑
- Ile ↑
Q. 5 The following statements are made regarding apoptosis in the nematode, C. elegans:
A. The human ortholog of C. elegans, CED-9 is overexpressed in a 8-cell lymphoma.
B. A ced-9(gain-of-function);ced-3(Loss-of-function) double mutant will have more than 947 non-gonadal cells.
C. If purified EGL-1 is added to a CED-9/CED-4 complex in vitro, the autocleavage of CED-3 does not occur.
D. CED-8 is a multi-spanning plasma membrane protein that is required for externalization of phosphatidylserine.
Which one of the following options represents all correct statements?
- A, B C and D
- A and B only
- A, B and D only
- B, C and D only
Answer : 3
Explanation:
- A: CED-9 ortholog is Bcl-2, overexpressed in lymphoma – True.
- B: Gain-of-function in ced-9 + loss-of-function in ced-3 prevents apoptosis – True.
- C: EGL-1 binding to CED-9 releases CED-4 to activate CED-3 – this would cause autocleavage, so the statement is False.
- D: CED-8 externalizes phosphatidylserine – True.
Q. 6 The following statements describe change in allele frequencies over time.
A. Fixation of an allele is purely by chance, while other alleles are lost.
B. Genetic drift can lead to the loss of certain alleles over time, reducing genetic diversity within the population.
C. Changes in allele frequencies are due to positive selection.
D. There is a pronounced effect in small populations, where random events can drastically alter allele frequencies.
Which one of the following options represents the combination of all correct statements if allele frequencies change purely due to genetic drift?
- A, B and C
- A, B and D
- B, C and D
- A, C and D
Answer : 2
Explanation:
Genetic drift involves random changes in allele frequency, especially in small populations. It can cause:
- Fixation of alleles by chance.
- Loss of genetic diversity.
Positive selection (adaptive evolution) is not part of genetic drift.
Q. 7 The figure given below represents the same data in six different ways. “A” represents the scatter plot of all data points and “B” is its corresponding box and whisker plot. “C” to “F” represent the same dataset with different measures of central tendency alongside various measures of variation (SEM – Standard Error of Mean, SD – Standard Deviation, Cl – 95% confidence interval).
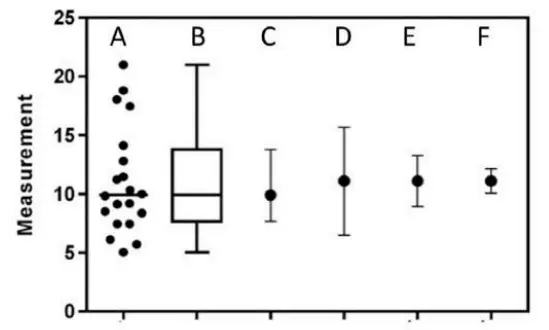
Which one of the following options is a correct representation of the data?
- C = Mean ± quartiles; D= Median ± SEM; E = Median ± Cl
- D = Mean± SD; E= Mean ± Cl ; F = Mean ± SEM
- C = Median with quartiles; D= Mean ± SEM; E = Mean with Cl
- D = Mean ± SEM; E = Mean± Cl; F = Mean ± SD
Answer : 2
Explanation :
- Standard Deviation (SD): It tells us how spread out the data points are around the mean. A large SD means the data are very spread out; a small SD means they are closely packed around the mean.
→ So, D = Mean ± SD shows how much the data vary. - Confidence Interval (CI): This tells us how confident we are that the true mean lies within a certain range. A 95% CI means there’s a 95% chance the real mean falls in that interval.
→ So, E = Mean ± CI shows the certainty of the mean. - Standard Error of Mean (SEM): This tells us how precise our mean is. It depends on both the SD and the number of data points (sample size). A smaller SEM means the mean is more precise.
→ So, F = Mean ± SEM shows the precision of the mean estimate.
Q. 8 The following statements were made regarding regulation of aging in C. elegans:
A. In most cells, p53 remains bound to a repressor protein to keep it inactive, which is activated under oxidative stress when DNA damage separates p53 from its repressor.
B. DAF-2 functions as an insulin-like growth factor receptor to block Forkhead transcription factor and increases the life span.
C. When DAF-2 is not active, cells reduce the production of DNA repair enzymes.
D. Dietary restriction increases mTORC1 activity, enhancing functional stem cells and longevity.
Which one of the following options has the combination of all correct statements?
- A and B
- B and C
- C and D
- A and D
Answer : 1
Explanation :
A is true: p53 gets activated under oxidative stress when it separates from its repressor.
B is true: DAF-2 blocks DAF-16 (a Forkhead transcription factor), and when DAF-2 is inactive, lifespan increases.
C is false: DAF-2 inactivity actually increases DNA repair via DAF-16, not decreases.
D is false: Dietary restriction actually reduces mTORC1 activity, which helps extend lifespan (the statement said the opposite).
Q. 9 In an experiment, FITC-CD4 and PE-CD8 were used to stain thymocytes. The cells were then run through a flow cytometer and the data were plotted as CD4 vs CD8 . The results are shown in the figure below and following statements are made:
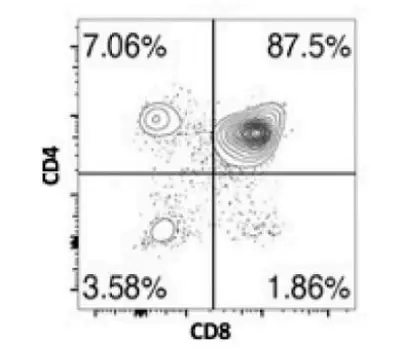
A. Rearrangement of TCR- β locus is initiated in cells included in the quadrant containing 3.58% of the population.
B. TCR-α locus rearrangement occurs in cells included in the quadrant containing 87 .5% population.
C. FITC-CD4 and PE-CD8 cannot stain the same cells.
D. Rearranged TCR-γδ receptor is expressed on 7.06% population of cells.
Which one of the following options represents the combination of all correct statements?
- A and B only
- A and D
- A, Band C
- B only
Answer : 1
Explanation:
A: “Rearrangement of TCR-β locus is initiated in cells included in the quadrant containing 3.58% of the population.” True: The 3.58% of the population represents the double-negative (DN) cells (CD4⁻CD8⁻). TCR-β rearrangement begins in this stage, before the cells move on to rearrange the TCR-α locus.
B: “TCR-α locus rearrangement occurs in cells included in the quadrant containing 87.5% of the population.” True: The 87.5% of the population represents double-positive (DP) cells (CD4⁺CD8⁺). At this stage, TCR-α rearrangement occurs after the TCR-β locus is rearranged in DN cells.
C: “FITC-CD4 and PE-CD8 cannot stain the same cells.” False: CD4 and CD8 can be co-expressed in double-positive (DP) thymocytes, meaning the same cells can be stained with both FITC-CD4 and PE-CD8.
D: “Rearranged TCR-γδ receptor is expressed on 7.06% population of cells.” Uncertain: The 7.06% might represent double-negative (DN) cells, but not all DN cells are γδ T cells. The statement doesn’t confirm this for sure.
Q. 10 Men suffering from enlarged prostate disease were prescribed drugs that would specifically target the androgen receptor (AR). While developing the drug, the following considerations were deliberated on:
A. Drugs should target the N-terminal domain of the AR.
B. Drugs should not target the NLS domain of the AR.
C. The drug should bind to the ligand-binding domain of the AR.
D. The drug should activate CYP17A1 to facilitate conversion of pregnenolone to DHEA.
Which one of the following combinations of considerations will develop the best drug for treatment of enlarged prostate?
- Aand B
- Band C
- C and D
- A and C
Answer : 4
Explanation:
C and D is not ideal because activating CYP17A1 would increase androgen production, which is undesirable. A and C would be the best combination for developing an effective drug. Targeting the ligand-binding domain (C) is a proven method, and avoiding the N-terminal domain (A) ensures that the drug does not interfere with essential receptor functions.
Also read :
CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 2
CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 3
CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 4
CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 5
CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 6
CSIR NET Life Science Previous Years Question Papers and answer keys
Join SACHIN’S BIOLOGY on Instagram or Facebook to receive timely updates and important notes about exams directly on your mobile device. Connect with Mr. Sachin Chavan, the founder of Sachin’s Biology and author of biologywala.com, who holds an M.Sc., NET JRF (AIR 21), and GATE qualifications. With SACHIN’S BIOLOGY, you can have a direct conversation with a knowledgeable and experienced.