CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 4

CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 4
Q. 1 Two newly identified proteins, X and Y, are tested for sequence-specific DNA binding activity. The results of an electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) with a labeled DNA fragment and proteins X and Y in various combinations are shown below.
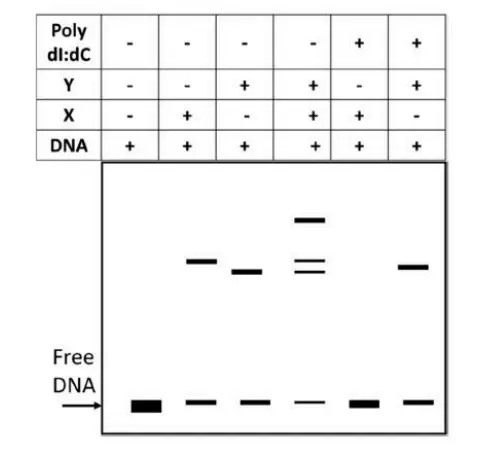
Poly dI:dC is a DNA duplex of polyinosine and polycytosine. Which one of the following options represents the correct interpretation of the results obtained?
- Both X and Y are sequence-specific DNA binding proteins.
- X does not bind to DNA and Y binds to specific sequence.
- Both proteins bind to DNA but Y binds in a sequence-specific manner.
- X competes with Y to bind the same sequence .
Answer : 3
Explanation:
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) is used to detect DNA-binding proteins. If a protein binds DNA non-specifically, poly dI:dC (used as a nonspecific competitor) will reduce the binding. In the gel, if Y still causes a shift even in the presence of poly dI:dC, it indicates sequence-specific binding. X shows a shift that is removed by poly dI:dC, suggesting non-specific binding. Hence, both bind DNA, but only Y is sequence-specific.
Q. 2 The following statements are about parental care and variance in reproductive success in a bird species.
A. If females provide more parental care than males, the variance in male reproductive success is significantly greater than that of females.
B. Where only males provide parental care, the variance in female reproductive success is significantly higher than that of males.
C. In the case of biparental care, the variance in male reproductive success is significantly greater than that of females .
D. In the case of biparental care, the variance in female reproductive success is significantly greater than that of males.
Select the option that identifies the combination of all correct statements.
- A and B
- A and C
- Band D
- C and D
Answer : 1
Explanation:
- Statement A: True. When females care more, males compete more for mates → higher variance in male reproductive success.
- Statement B: True. When only males provide care, females compete for them → higher variance in female reproductive success.
- Statements C & D: False. In biparental care, both sexes contribute equally, usually reducing variance in both.
Q. 3 A student used four 20~mer oligos to amplify DNA (using a regular Taq DNA polymerase) from a wild type (WT), a homozygous mutant having a deletion of the gene (del), and from the heterozygous mutant (het), as shown in the figure below.
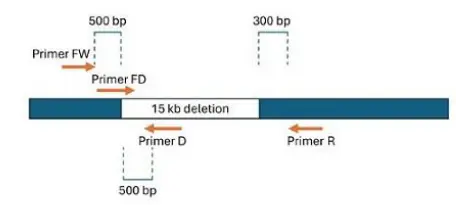
Agarose gel electrophoresis profiles, using all four primers simultaneously, on each template are shown below. Which one of the options given below represents the correct profile?

Answer : 2
Explanation:
You’re using 4 primers to test 3 types of DNA:
- WT (Wild Type) – normal gene
- Del (Deletion) – gene is deleted
- Het (Heterozygote) – one normal copy, one deleted copy
The 4 primers are designed so that:
- If the gene is present (WT), one specific band is seen.
- If the gene is deleted (Del), a different band appears (from the flanking region).
- If the sample is heterozygous (Het), both bands will appear – one for WT, one for Del.
So, on a gel:
- WT = 1 band
- Del = 1 band (different size from WT)
- Het = 2 bands (both WT and Del)
Lane 2 in the gel shows 2 bands, so it must be the heterozygote.
Q. 4 The table below lists selected bird species (Column X) and their possible habitats (Column Y).
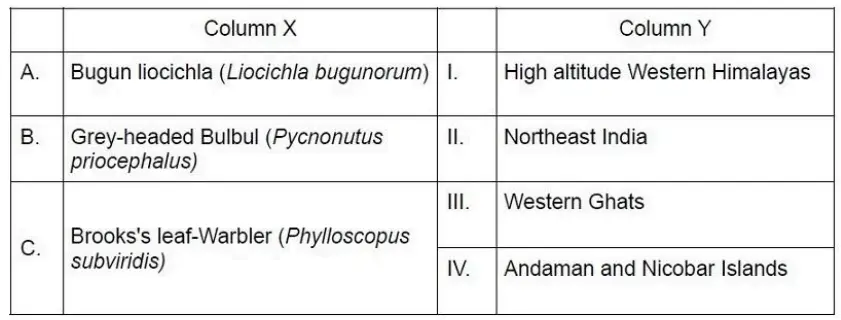
Which one of the following options represents all correct matches between Column X and Column Y?
- A-I B-II C-III
- A-III B-I C-IV
- A-IV B-II C-III
- A-II B-III C-I
Answer : 4
Q. 5 Shown in the table below are the enzymes (Column X) involved in the biosynthesis of listed phytohormones (Column Y).
| Column X | Column Y |
|---|---|
| A. Carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase | i. Brassinosteroid |
| B. ER localized cytochrome P450 monoxygenase | ii. Strigolactone |
| C. ACC oxidase | iii. Abscisic acid |
| D. 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | iv. Ethylene |
Which one of the following options represents al l correct matches between Column X and Column Y?
- A (ii) B (i) C (iii) D (iv)
- A (i) B (ii) C (iv) D (iii)
- A (iv) B (ii) C (iii) D (i)
- A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
Answer : 4
Explanation:
- A. Carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase → Strigolactone (ii)
- B. ER-localized cytochrome P450 → Brassinosteroid (i)
- C. ACC oxidase → Ethylene (iv)
- D. 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase → Abscisic acid (iii)
Each enzyme catalyzes a key step in its respective hormone biosynthesis.
CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 3
Q. 6 Three strands of a beta-sheet of 4 peptides are hydrogen bonded with the orientation of the strands (parallel or antiparallel denoted by the arrowheads) as shown in the figure. Each strand consists of identical residues, where N and C represent terminal residues of the peptide. The three strands of each peptide are linked by amino acid sequences of the smallest length possible.
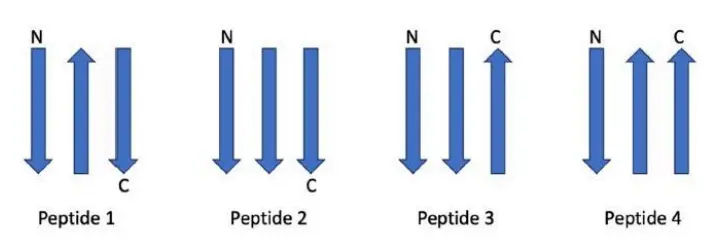
Which one of the following options is correct regarding the length of the peptides 1 to 4?
- (Peptide 1 = Peptide 2) < Peptide 3 < Peptide 4
- Peptide 1 < (Peptide 3 = Peptide 4) < Peptide 2
- Peptide 1 < Peptide 3 < Peptide 4 < Peptide 2
- Peptide 1 < Peptide 2 < Peptide 3 < Peptide 4
Answer : 2
Explanation –
In a beta-sheet, the way strands are connected matters:
- Antiparallel strands (arrows facing opposite directions) are closer together, so the loops connecting them are short.
- Parallel strands (arrows in the same direction) are farther apart, so the loops must be longer.
So, if a peptide has:
- More parallel connections, it needs more amino acids (longer).
- More antiparallel connections, it can be shorter.
By looking at the strand arrangement in the diagram (not shown), we can tell the relative length of each peptide. That’s why the correct answer shows the shortest to longest peptide based on how their strands are connected.
Q. 7 The magnetic field generated from an electromagnet is used in the transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) of the brain. The following statements suggest some features of TMS:
A. The magnetic field generated in TMS induces an electrical field in the underlying brain area.
B. The electrical field in the brain area alters the membrane potential of the neurons ln that locality causing them to depolarize synchronously, which in turn, may change the probability of the firing of neurons.
C. In cognitive neuroscience research , TMS may be used as a tool to induce a ‘virtual lesion’ in a selected region of the cerebral cortex.
D. TMS is safe and non-invasive but the neuronal activity of the stimulated area is disrupted for a long period of time.
Which one of the following options represents the combination of all correct
statements?
- A, B and C
- B C and D
- C and D only
- A only
Answer : 1
Explanation:
A: True – TMS uses magnetic fields to induce electric currents in the brain.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) works by using a magnetic field to generate electric currents in specific areas of the brain. This is how it affects brain activity.
B: True – The electric field alters neuronal membrane potential, leading to depolarization.
The electric current from the magnetic field changes the electrical charge across the neuron’s membrane. This can make the neuron more likely to fire, which is called depolarization.
C: True – TMS can temporarily block activity in specific areas (“virtual lesion”).
By targeting certain areas of the brain, TMS can “shut down” or block activity in those areas temporarily. This is sometimes referred to as creating a “virtual lesion,” as if a part of the brain was damaged.
D: False – TMS effects are short-lived; not a long-term disruption.
While TMS can temporarily change brain activity, its effects don’t last long. It’s not a permanent disruption to brain function.
So, TMS is a tool that temporarily alters brain activity using magnetic fields and electric currents, but its effects are short-term.
Q. 8 The table below gives the avian community composition of three communities (X, Y, Z), where ‘1’ indicates the presence of the species in the community and O’ indicates its absence.
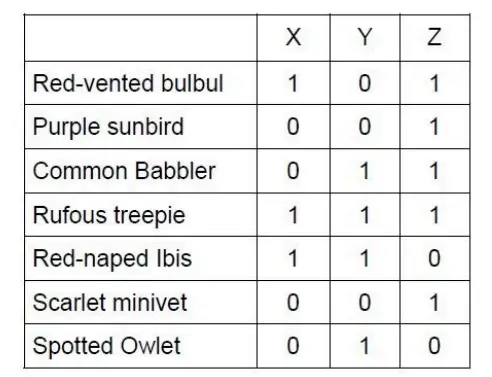
Select the option that lists the correct order of similarity between pairs of communities based on Sorensen’s coefficient of similarity.
- (X, Y) > (Y ,Z) > (X,Z)
- (X,Y) > (X,Z) > (Y,Z)
- (Y,Z) > (X,Z) > (X,Y)
- (X,Y) = (X,Z) = (Y,Z)
Answer : 2
Explanation :
Sorensen’s Coefficient Formula:
S = (2 × number of shared species) / (total species in both communities)
1. (X, Y)
- Shared species: Rufous treepie, Red-naped Ibis → 2 shared
- Total in X = 3 (bulbul, treepie, ibis)
- Total in Y = 4 (babbler, treepie, ibis, owlet)
- Combined total = 3 + 4 = 7
🧮 S(X,Y) = (2 × 2) / 7 = 4 / 7 ≈ 0.571
2. (X, Z)
- Shared species: Red-vented bulbul, Rufous treepie → 2 shared
- Total in X = 3
- Total in Z = 5 (bulbul, sunbird, babbler, treepie, minivet)
- Combined = 3 + 5 = 8
🧮 S(X,Z) = (2 × 2) / 8 = 4 / 8 = 0.5
3. (Y, Z)
- Shared species: Common babbler, Rufous treepie → 2 shared
- Total in Y = 4
- Total in Z = 5
- Combined = 4 + 5 = 9
🧮 S(Y,Z) = (2 × 2) / 9 = 4 / 9 ≈ 0.444
✅ Final Order of Similarity:
- (X,Y) = 0.571
- (X,Z) = 0.5
- (Y,Z) = 0.444
Correct answer: (X,Y) > (X,Z) > (Y,Z)
Q. 9 In Drosophila melanogaster, a cross was performed, and the resulting progeny are indicated below.
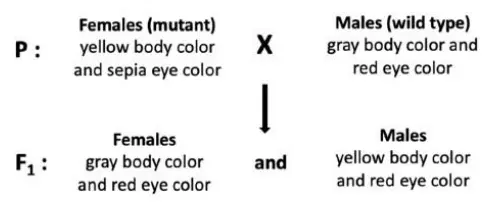
The F1 progeny were sib-mated and the F2 progeny were analyzed . The following statements were made based on the above crosses and analysis of the progeny:
A. The mutation leading to sepia eye color is located on an autosome.
B. Yellow body is a dominant phenotype.
C. One fourth of the F2 progeny will be males with yellow body color.
D. In this dihybrid cross, as the F2 progeny do not show a 9:3:3:1 typical Mendelian ratio, the two genes can be assumed to be linked.
Which one of the following options correctly identifies each statement as True (T) or False (F) from A to D, respectively?
- T, F, T, F
- F, T, T, F
- T, T, F, F
- F, F, T, T
Answer : 1
Explanation:
A: True – Sepia eye is autosomal (not sex-linked).
B: False – Yellow body is recessive and X-linked, not dominant.
C: True – ¼ of F2 are yellow-bodied males, as expected from X-linked inheritance.
D: False – A non-9:3:3:1 ratio doesn’t prove linkage; other reasons like epistasis could cause it.
Q. 10 A researcher placed plant cells in a hypertonic solution to cause the cells to shrink. The following statements are made regarding the plasmolyzed cells.
A. Microtubules are lost in the plasmolyzed cells.
B. Protoplasts are retracted in the plasmolyzed cells.
C. Hechtian strands are lost during plasmolysis.
D. Patches of plasma membrane remain affixed to the wall.
Which one of the following options represents the combination of all correct
statements?
- A, B and C
- B and C only
- A, C and D
- B and D
Answer : 4
Explanation:
A is false because during plasmolysis, microtubules are not typically lost. They may rearrange or become less organized, but they are not completely absent from the cell.
B is true because in a hypertonic solution, water moves out of the plant cell, causing the protoplast (the living part of the cell including the membrane and cytoplasm) to shrink and pull away from the rigid cell wall.
C is false because Hechtian strands are actually observed during plasmolysis. These are thin strands that connect the protoplast to the cell wall and remain visible as the protoplast shrinks.
D is true because even after the protoplast pulls away, some parts of the plasma membrane remain attached to the cell wall. These attachment points are where Hechtian strands are often seen.
Also read :
CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 5
CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 3
CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 2
CSIR NET Life Science Dec 2024 Answer Key (Parts C) – Complete Explanations! Part 1
CSIR NET Life Science Previous Years Question Papers and answer keys
Join SACHIN’S BIOLOGY on Instagram or Facebook to receive timely updates and important notes about exams directly on your mobile device. Connect with Mr. Sachin Chavan, the founder of Sachin’s Biology and author of biologywala.com, who holds an M.Sc., NET JRF (AIR 21), and GATE qualifications. With SACHIN’S BIOLOGY, you can have a direct conversation with a knowledgeable and experienced.
![[Download] Plant Systematics by Simpson PDF Book 3rd edition 9 [Downlaod] Plant Systematics by Simpson PDF Book 3rd edition](https://biologywala.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Downlaod-Plant-Systematics-by-Simpson-PDF-Book-3rd-edition-520x245.webp)

