Genetic Terminologies class 12 notes PDF Download

Genetic Terminologies class 12 notes is a helpful resource for students who want to revise important concepts quickly and clearly. Understanding genetics can feel tricky at first, especially with so many new terms and definitions to remember. To make your preparation easier, we’ve created Class 12 Genetics Terminology Notes in a simple and clear format. These notes cover all the important terms you need to know for exams, explained in easy language with examples where necessary. At the end, you can also download the PDF version for quick revision anytime, anywhere. In this blog on Genetic Terminologies class 12 notes PDF Download, we will see all the terminologies required for the proper understanding of genetics.
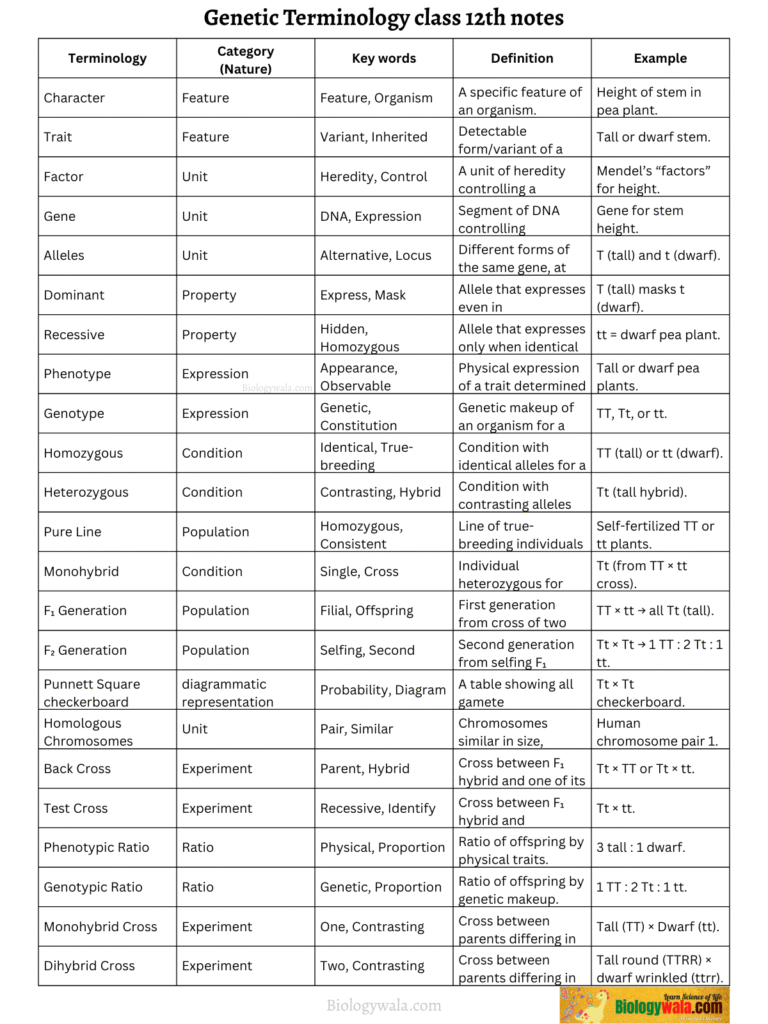
Genetic Terminologies:
1. Character
A specific feature of an organism, e.g., height of the stem in a plant.
2. Trait
A detectable form or variant of a character that is inherited, e.g., tall or dwarf.
3. Factor
A unit of heredity present in an organism that controls the inheritance and expression of a character. These factors are passed from one generation to the next through gametes. Today, these factors are known as genes.
4. Gene
A specific segment of DNA that controls the inheritance and expression of a character.
5. Alleles (Allelomorphs)
Different alternative forms of the same gene are called alleles. They are found at the same position (locus) on homologous chromosomes. Controls the trait of the character; the term “allele” is a shortened form of “allelomorph.”
6. Dominant
An allele that expresses itself even when paired with a different allele (heterozygous condition). It is the allele that expresses itself in the F₁ generation and masks the effect of the other allele.
7. Recessive
An allele that remains unexpressed in the presence of a dominant allele (heterozygous condition). It can only express when two identical copies are present (homozygous condition). This allele does not appear in the F₁ hybrid.
8. Phenotype
The observable (external) physical appearance of an individual for a particular trait. The combination of alleles determines it.
Example: In pea plants, tall and dwarf are two phenotypes. Tall may result from TT or Tt, while dwarf results from tt.
9. Genotype
The genetic constitution or makeup of an organism with respect to a trait. It represents the allele combination an individual carries.
Example: A tall pea plant may have genotype TT or Tt, while a dwarf plant has tt.
10. Homozygous (pure)
An individual having identical alleles for a trait is called homozygous. It breeds true for that trait and produces only one type of gamete.
Example: Tall (TT) or dwarf (tt).
11. Heterozygous
An individual having contrasting alleles for a trait is called heterozygous. It does not breed true and produces two types of gametes. Such individuals are also called hybrids.
Example: F₁ generation hybrid Tt in pea plants.
12. Pure Line
A group of individuals that are homozygous and true-breeding for one or more traits. They consistently pass the same character to the next generation. Such a line originates from a single homozygous parent through self-fertilisation.
13.Monohybrid
An individual heterozygous for a single trait, produced by crossing two pure parents that differ in one pair of contrasting characters.
14. F₁ Generation
Latin word filius (son) or filia (daughter). The first filial generation consists of all offspring produced from a cross between two pure parents with contrasting traits. It represents the first generation from such a mating.
15. F₂ Generation
The second filial generation produced by self-fertilisation (inbreeding) of F₁ offspring.
Example: Crossing two F₁ hybrids (Tt × Tt) produces the F₂ generation.
16. Punnett Square (Checkerboard)
A probability table that shows all possible combinations of gametes from opposite parents. It is a diagram used to predict the types and ratios of offspring from a genetic cross.
17. Homologous Chromosomes:
Chromosomes that are similar in size, structure, and genetic content, found in diploid cells. They pair (synapse) during meiosis.
18. Back Cross
A cross between an F₁ hybrid and either of its parents. Example: Tt × TT (pure tall) or Tt × tt (pure dwarf).
19. Test Cross
A cross between an F₁ hybrid and a homozygous recessive parent, used to determine whether the hybrid is homozygous or heterozygous.
Example: Tt × tt.
20. Phenotypic ratio
It is the ratio of the offspring produced in F2 and subsequent generations with respect to their physical appearance, e.g. 3Tall: 1 dwarf, is F2 ‘Phenotypic ratio’ in a monohybrid cross.
21. Genotypic ratio
It is the ratio of the offspring produced in the F2 and subsequent generations with respect to their genetic makeup, e.g. 1 TT : 2Tt : 1 tt, is F2 genotypic ratio in a monohybrid cross.
22. Monohybrid cross
A cross between parents which differ in only one heritable trait is called a monohybrid cross. e.g. cross of pure tall and pure dwarf plants. Mendel performed the monohybrid cross between two pea plants with only one pair of contrasting characters.
23. Dihybrid cross
A cross between parents differing in two heritable traits is called a dihybrid cross, e.g. cross of a pure tall, round-seeded plant with a dwarf, wrinkled-seeded plant. Mendel also performed the dihybrid cross between pea plants that differed in two pairs of contrasting characters.
Below is the link to Download Genetic Terminologies class 12 notes PDF :
Join SACHIN’S BIOLOGY on Instagram or Facebook to receive timely updates and important notes about exams directly on your mobile device. Connect with Mr. Sachin Chavan, the founder of Sachin’s Biology and author of biologywala.com, who holds an M.Sc., NET JRF (AIR 21), and GATE qualifications. With SACHIN’S BIOLOGY, you can have a direct conversation with a knowledgeable and experienced professional in the field of biology. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to enhance your exam preparation!

![[PDF] Molecular Basis of Inheritance class 12th Complete Notes 4 DOWNLOAD [PDF] Molecular Basis of Inheritance class 12th Complete Notes](https://biologywala.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/DOWNLOAD-PDF-Molecular-Basis-of-Inheritance-class-12th-Complete-Notes.png)