General characteristics of algae: 7 classes
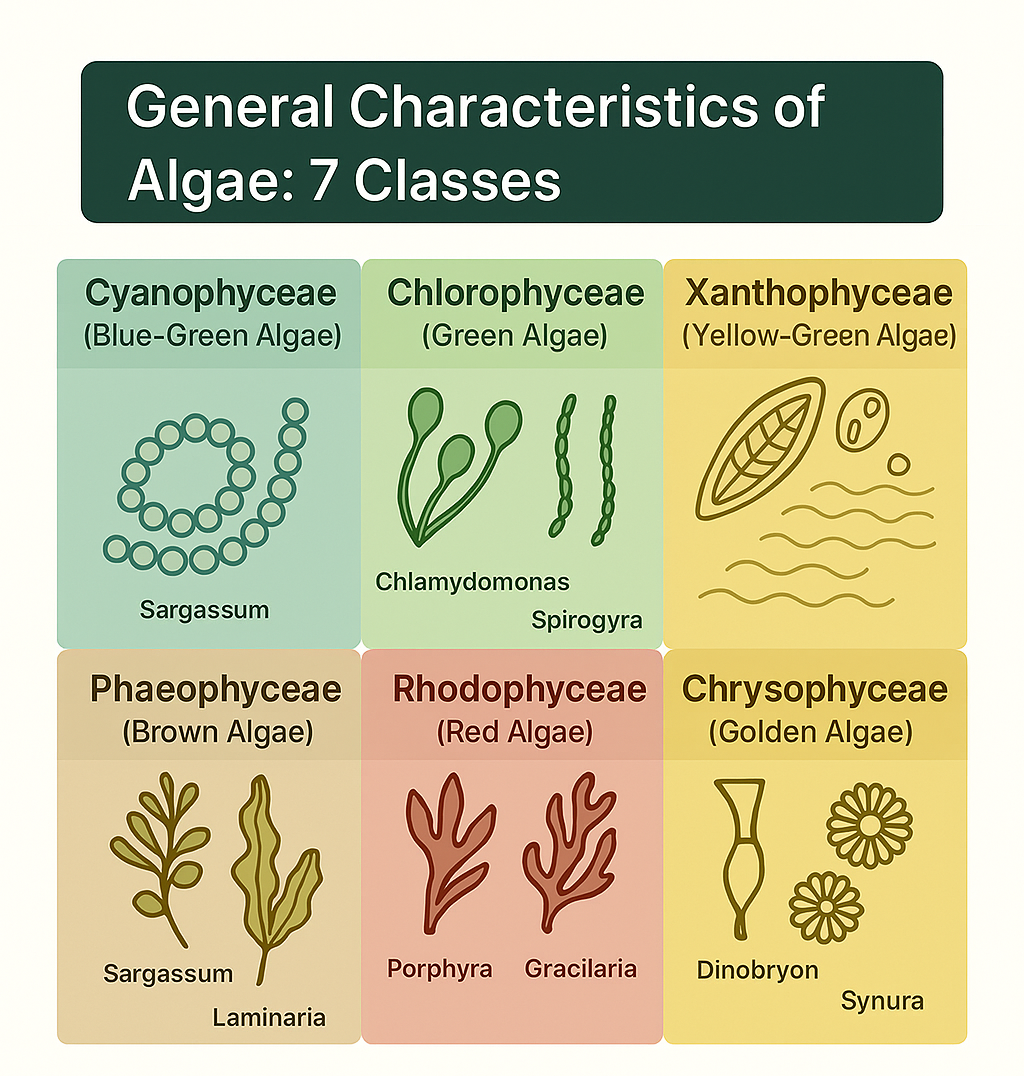
Algae, diverse photosynthetic organisms found in various habitats, encompass seven major classes: Cyanophyceae (blue-green algae), Chlorophyceae (green algae), Xanthophyceae (yellow-green algae), Bacillariophyceae (diatoms), Phaeophyceae (brown algae), Rhodophyceae (red algae), and Chrysophyceae (golden algae). Each class exhibits unique pigments, cell structures, and life cycle characteristics, contributing to their ecological significance as primary producers and essential components of aquatic food webs.
1. Cyanophyceae (Blue-Green Algae):
- Habitat: Primarily freshwater, also found in marine and terrestrial environments.
- Pigments: Chlorophyll a, phycocyanin (blue), phycoerythrin (red).
- Storage Product: Cyanophycean starch.
- Cell Wall: Peptidoglycan, mucilage.
- Flagella: Absent.
- Reproduction: Primarily asexual (binary fission, fragmentation, hormogonia), rare sexual reproduction.
- Examples: Nostoc, Anabaena, Spirulina.
2. Chlorophyceae (Green Algae):
- Habitat: Freshwater, marine, and terrestrial.
- Pigments: Chlorophyll a, b.
- Storage Product: Starch.
- Cell Wall: Cellulose.
- Flagella: Present in some (zoospores, gametes).
- Reproduction: Asexual (zoospores, aplanospores) and sexual (isogamy, anisogamy, oogamy).
- Examples: Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra, Volvox.
3. Xanthophyceae (Yellow-Green Algae):
- Habitat: Primarily freshwater.
- Pigments: Chlorophyll a, c, carotenoids (yellow).
- Storage Product: Chrysolaminarin.
- Cell Wall: Cellulose, silica.
- Flagella: Present in some (zoospores, gametes).
- Reproduction: Asexual (zoospores, aplanospores) and sexual (isogamy, anisogamy, oogamy).
- Examples: Vaucheria.
4. Bacillariophyceae (Diatoms):
- Habitat: Freshwater and marine.
- Pigments: Chlorophyll a, c, fucoxanthin (brown).
- Storage Product: Chrysolaminarin.
- Cell Wall: Silica frustule (two halves).
- Flagella: Absent.
- Reproduction: Asexual (cell division) and sexual (oogamy).
- Examples: Navicula, Pinnularia.
5. Phaeophyceae (Brown Algae):
- Habitat: Mostly marine.
- Pigments: Chlorophyll a, c, fucoxanthin (brown).
- Storage Product: Laminarin, mannitol.
- Cell Wall: Cellulose, algin.
- Flagella: Present in some (zoospores, gametes).
- Reproduction: Asexual (fragmentation, zoospores) and sexual (isogamy, anisogamy, oogamy).
- Examples: Sargassum, Fucus, Laminaria (kelp).
6. Rhodophyceae (Red Algae):
- Habitat: Mostly marine.
- Pigments: Chlorophyll a, phycoerythrin (red), phycocyanin (blue).
- Storage Product: Floridean starch.
- Cell Wall: Cellulose, agar, carrageenan.
- Flagella: Absent.
- Reproduction: Asexual (monospores, tetraspores) and sexual (complex life cycle).
- Examples: Porphyra, Gracilaria, Gelidium.
7. Chrysophyceae (Golden Algae):
- Habitat: Primarily freshwater, some marine.
- Pigments: Chlorophyll a, c, fucoxanthin, carotenoids (golden-brown).
- Storage Product: Chrysolaminarin, oil.
- Cell Wall: Cellulose, sometimes with silica scales.
- Flagella: One or two flagella, sometimes absent.
- Reproduction: Asexual (cell division, statospores) and sexual (rare).
- Examples: Dinobryon, Synura.
A comparative Chart of all the characters for all 7 classes of Algae:
| Characteristic | Cyanophyceae | Chlorophyceae | Xanthophyceae | Bacillariophyceae | Phaeophyceae | Rhodophyceae | Chrysophyceae |
| Habitat | Freshwater, marine, terrestrial | Freshwater, marine, terrestrial | Primarily freshwater | Freshwater, marine | Mostly marine | Mostly marine | Primarily freshwater, some marine |
| Pigments | Chlorophyll a, phycocyanin, phycoerythrin | Chlorophyll a, b | Chlorophyll a, c, carotenoids | Chlorophyll a, c, fucoxanthin | Chlorophyll a, c, fucoxanthin | Chlorophyll a, phycoerythrin, phycocyanin | Chlorophyll a, c, fucoxanthin, carotenoids |
| Storage Product | Cyanophycean starch | Starch | Chrysolaminarin | Chrysolaminarin | Laminarin, mannitol | Floridean starch | Chrysolaminarin, oil |
| Cell Wall | Peptidoglycan, mucilage | Cellulose | Cellulose, silica | Silica frustule | Cellulose, algin | Cellulose, agar, carrageenan | Cellulose, sometimes with silica scales |
| Flagella | Absent | Present in some | Present in some | Absent | Present in some | Absent | One or two flagella, sometimes absent |
| Reproduction | Asexual (binary fission, fragmentation, hormogonia), rare sexual | Asexual (zoospores, aplanospores) and sexual | Asexual (zoospores, aplanospores) and sexual | Asexual (cell division) and sexual (oogamy) | Asexual (fragmentation, zoospores) and sexual | Asexual (monospores, tetraspores) and sexual | Asexual (cell division, statospores) and sexual (rare) |
| Examples | Nostoc, Anabaena, Spirulina | Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra, Volvox | Vaucheria | Navicula, Pinnularia | Sargassum, Fucus, Laminaria | Porphyra, Gracilaria, Gelidium | Dinobryon, Synura |