Virus: Structure, Types, Classification And Diseases
Introduction: Virus: Structure, Types, Classification And Diseases
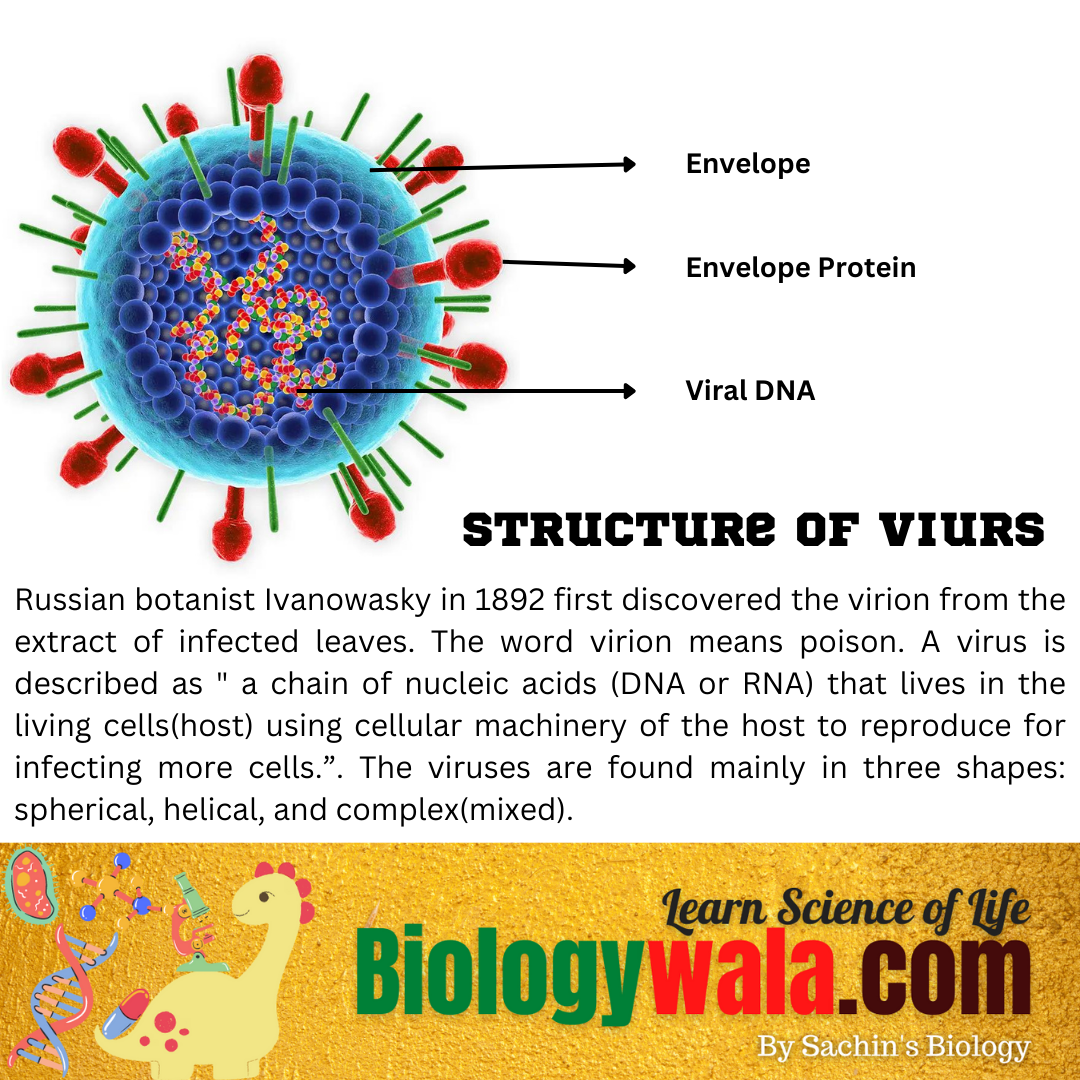
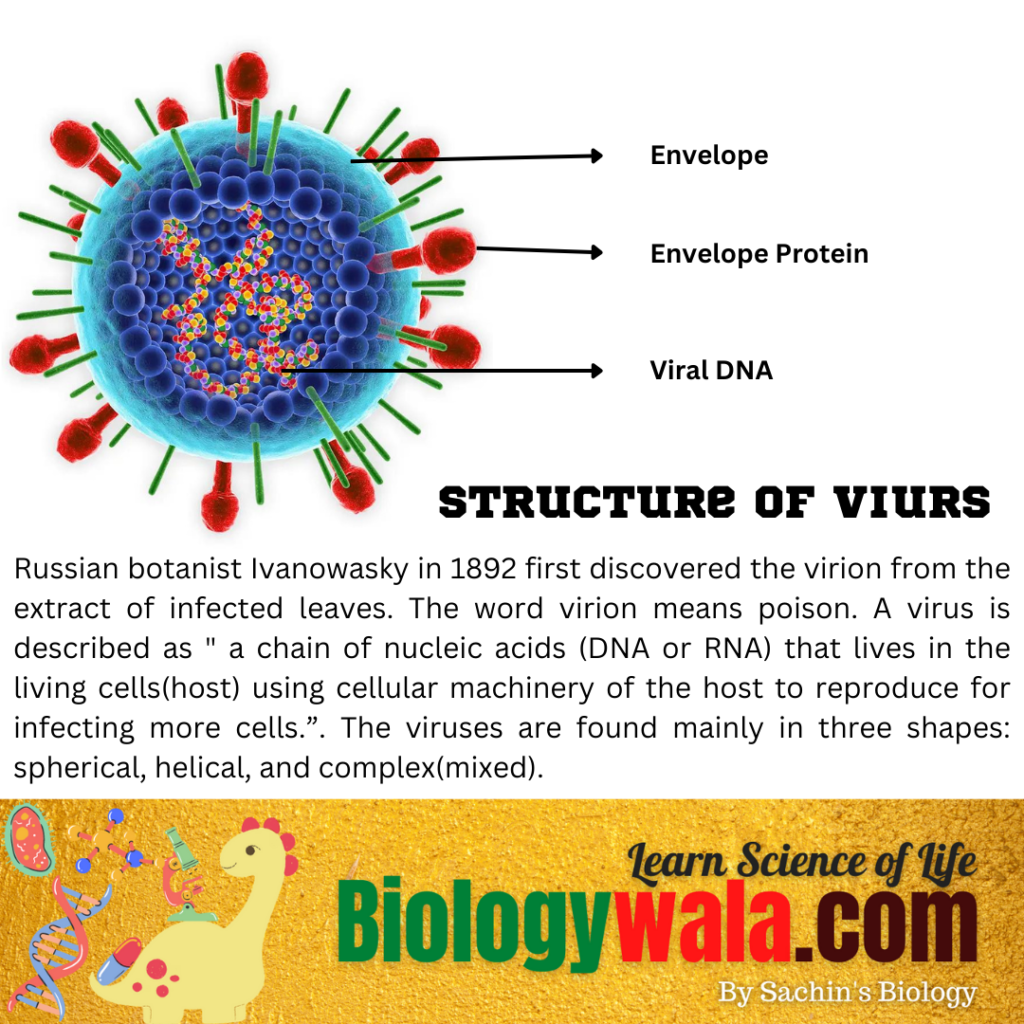
Russian botanist Ivanowasky 1892 first discovered the virion from the extract of infected leaves. The word virion means poison.
A virus is described as :
” a chain of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) that lives in the living cells(host) using cellular machinery of the host to reproduce for infecting more cells.”.
Definition
The viruses are found mainly in three shapes: spherical, helical, and complex(mixed). A virus is often surrounded by a protein coat which allows it to survive inside the host. Viruses contain a nucleic acid core that protects the virus from the action of the host cell.
Structure of virus
A virus can take a variety of different structures. It varies in size and shape. The smallest virus is about 17nm in size while the largest one is about 1500nm which is extremely minute. It is a microscopic organism that requires techniques like SEM and TEM for its observational studies.
There are specific viruses that only infect and replicate inside bacterial cells called phages or Bacteriophages. They possess a unique structure with a complex variety of specialized parts.
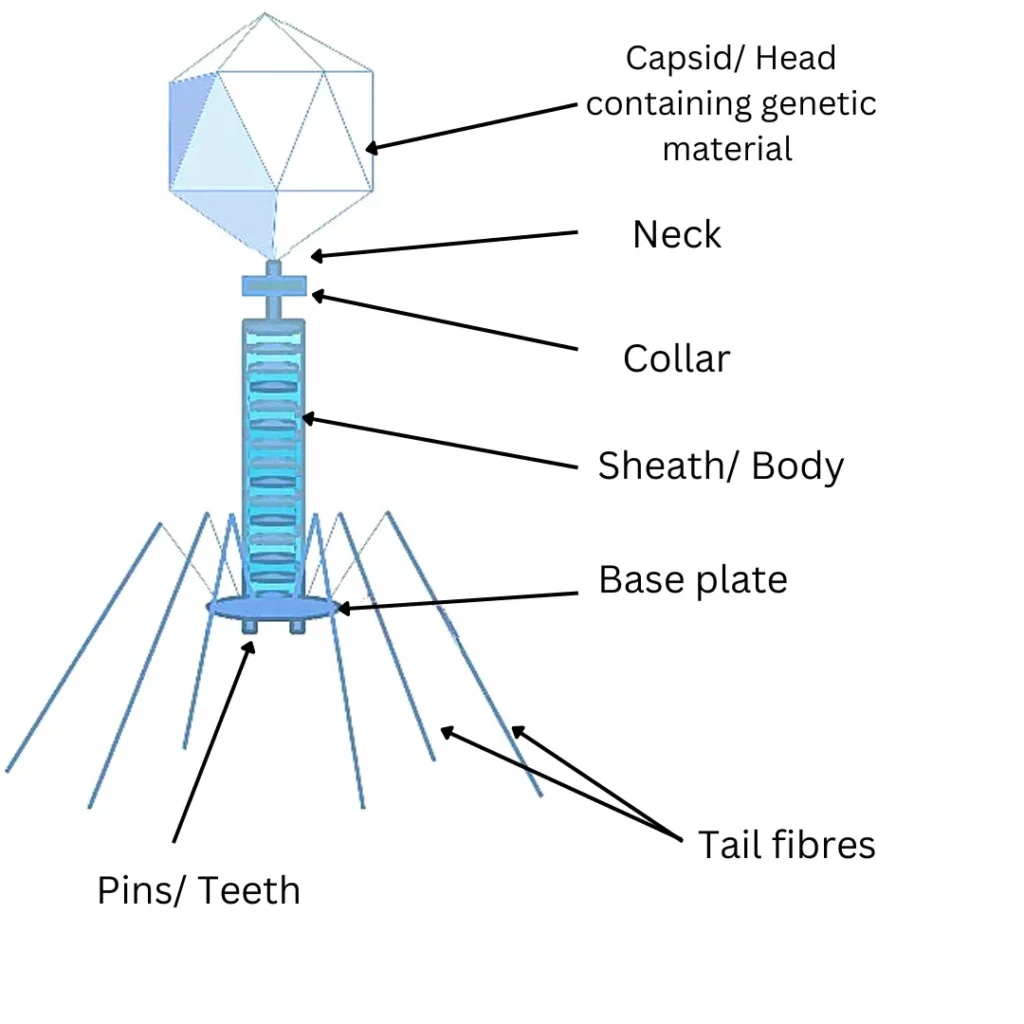
1. The head portion of a bacteriophage contains a viral genome.
2. The collar, sheath, base plate, and tail fibres play role in infecting and attaching to the host. It attaches and infects the bacterial cell genome.
3. The tail fibres gasp bacterial cells pulling the base plate to the cell wall or cell membrane.
4. The sheath and collar puncture the cell and deposit its genetic material (DNA or RNA) into the host cell.
5. In some plant viruses, the virus is passed from cell to cell within the plant.
6. When seeds are formed in plants the viruses spread to seeds and live their entire existence without the need for a protein coat.
Classification of viruses:
Viruses are classified on the basis of two different categories –
1. On the basis of the host
2. On the basis of genetic material
Based on these two different modes of classification viruses are classified into several subtypes.
On the basis of the host:
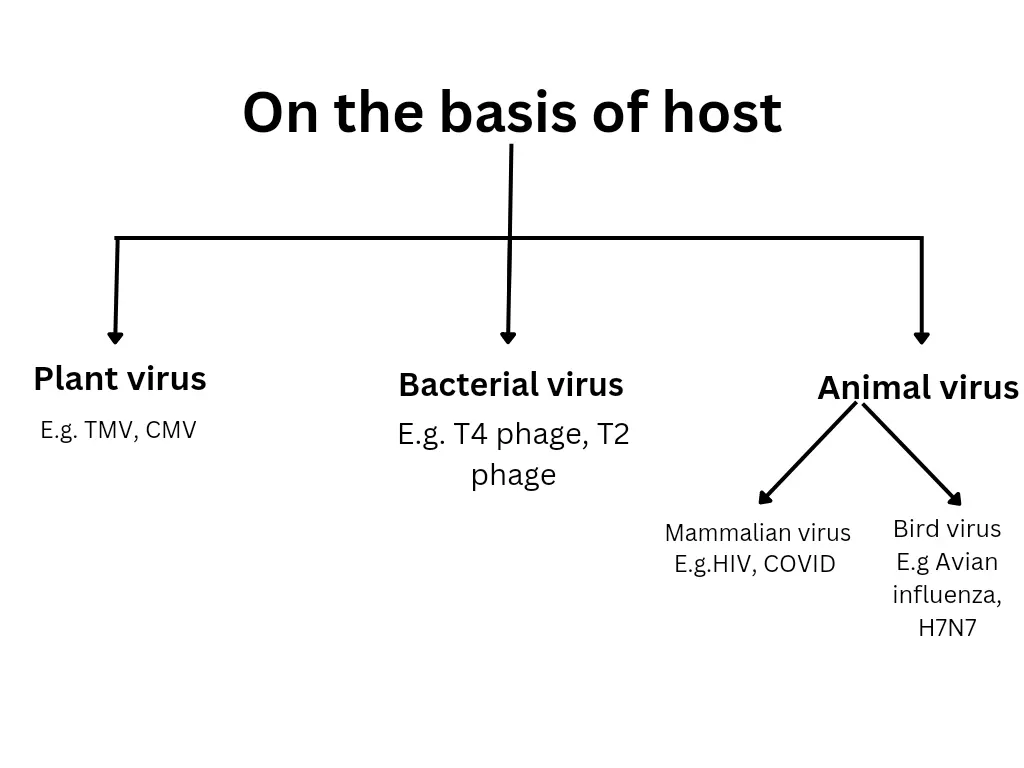
1. Plant viruses – These are the intracellular parasites that infect plants. These viruses multiply by infecting the plant cells and utilizing the plant cell’s genetic replication machinery. Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) is the first plant virus was discovered. E.g. TMV, Cucumber mosaic virus(CMV), Yellow vein mosaic virus(YVMV), Potato virus Y.
2. Bacterial viruses – The viruses which infect the bacteria are called bacterial viruses or bacteriophages. These viruses are widely present in the soil and the intestines of animals. E.g. T4 phage, T2 phage, P1 phage, M13 bacteriophage.
3. Animal viruses – These are the viruses that infect and cause diseases in humans and other animals. It includes mammalian viruses like HIV and Covid 19 and bird viruses like Avian influenza(bird flu) and H7N7.
On the basis of genetic material:
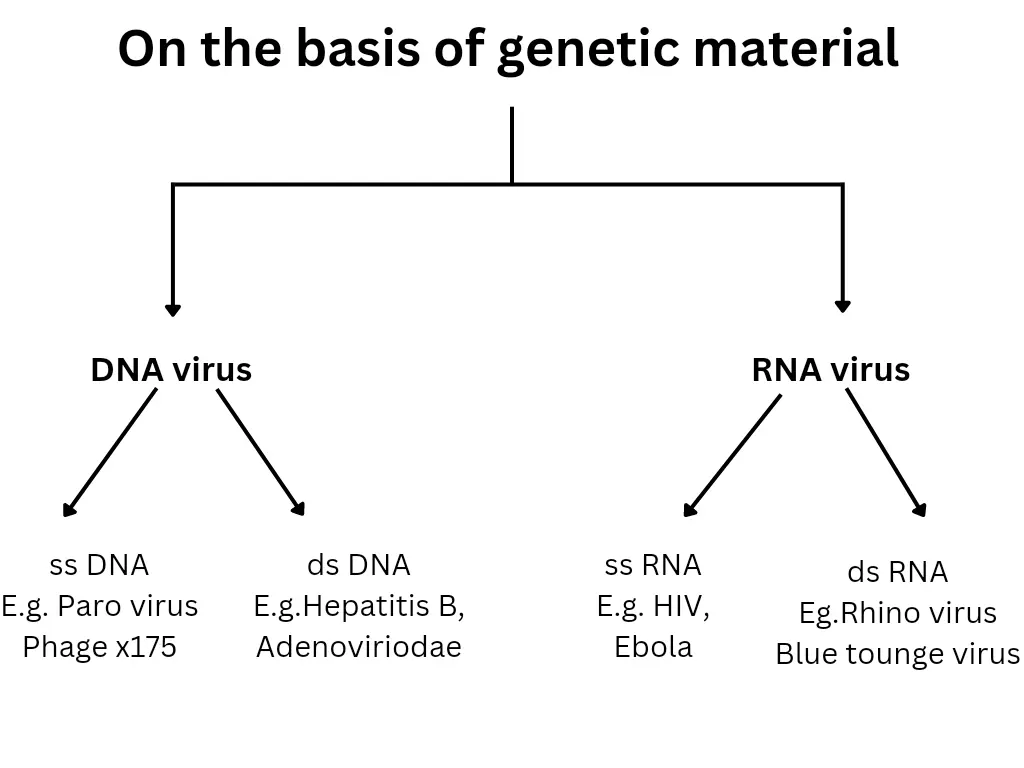
Virus possesses DNA or RNA as genetic material in their genome. Based on this they have been classified into 2 main types –
1. DNA virus – DNA virus contains DNA as their genetic material and replicates using DNA polymerase. They are divided into double-stranded (ds) DNA viruses and single-stranded (ss) DNA viruses. E.g. Herpesvirus, smallpox virus, and adenovirus. Large DNA viruses have double-stranded DNA while small DNA viruses have circular/single/ double-stranded DNA.
2. RNA virus – It is a virus that has RNA as its genetic material. It is usually single-stranded (ss) but sometimes double-stranded(ds) also. E.g. Hepatitis C virus, TMV, CMV. RNA viruses replicate using virally encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase(RdRp). There are three types of RNA that must be synthesized during replication: the genome, a copy of the genome, and mRNAs.
Viral diseases of plants:
Tobacco mosaic disease –
- Causal organism – Tobacco mosaic virus or Nicotiana virus 1
- Host – Nicotiana tabacum
- Infected part – Stem and leaves. It can also spread through the phloem of plants and by direct contact with nearer infected plants.
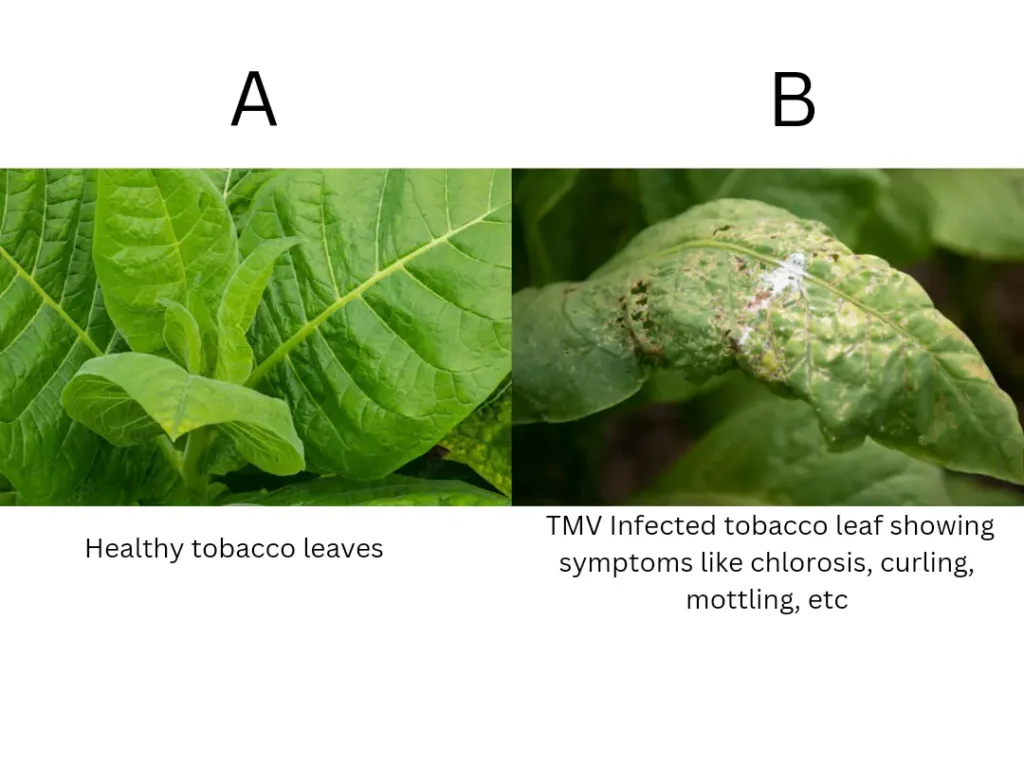
The disease is first reported by Adolph Mayer in 1882. The virus infects tobacco and the members of the family Solanaceae and it is a single-stranded (ss) RNA virus. The virus is transmitted through sap and wounds and moves from cell to cell through plasmodesmata infecting every cell. The transmission of the virus also takes place through mechanical means and by wind and water.
Symptoms –
- Light discolouration along the veins of young leaves takes place first.
- The mosaic symptoms along with blistering of leaves are observed due to the rapid growth of dark green tissue.
- Plants become stunted.
- Leaves become narrow, puckered, thin, and malformed.
- Leaves show chlorosis, curling, mottling, dwarfing, blistering, etc.
- Partial sterility of pollen takes place due to disease.
Control measures –
- Sanitation: Thoroughly weeding of fields and rouging of diseased plants and weeds in the field should be done.
- Crop rotation – Two years of crop rotation avoids infection from soil dramatically.
- If the plants are inoculated with a milder strain cross protection is reported. Tobacco plants are produced with the gene coding of the TMV coat protein.
- As TMV is inhibited by whole milk(Hare and Lucas, 1959) some states in the USA recommended spraying milk on plants before transplanting or handling the plants.
- Use of disease-resistant or tolerant tobacco varieties.
Cucumber mosaic disease-
- Host – Cucumis sativus
- Causal organism- Cucumber mosaic virus
- Infected part – Stem, leaves, and fruits
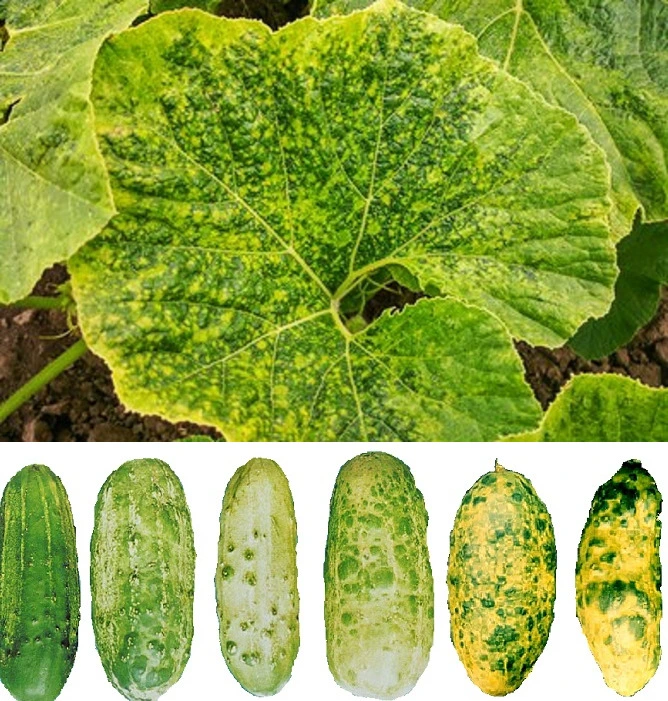

Symptoms –
- Young leaves become mottled after 5 days of infection.
- Leaves become distorted, and wrinkled forming rosette-like structures near the ground.
- The older leaves develop necrosis on the margins that spread to entire leaves.
- Pale green or white patches develop on fruits and they become odd-shaped. Fruits turn bitter and get spongy.
- CMV is a single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) virus that infects plants in the early or young stages.
Control measures –
- Development of genetic resistance in plants.
- Eradication of infected plants.
- Use of trap crop method to keep parts away from nearby crops.
- Use of insecticides to control the aphid population.
- Crop rotation can reduce down chances of reinfection.
- Eradication of perennial weed may decrease the chances of reinfection.
Comment below if you like the blog and if this blog helped you, it means a lot and will give us the energy to work with the same enthusiasm in future! This is it for today. See you in the Next article, Thank you!
You will also like :
Download the Free Book of Plant Physiology by Taiz and Zieger 6th edition
[Download] Plant Systematics by Gurcharan Singh PDF Book 3rd edition
If you want important notes and updates about exams on your mobile then you can join SACHIN’SBIOLOGY on Instagram or Facebook and can directly talk to the founder of Sachin’s Biology and Author of biologywala.com Mr Sachin Chavan M.Sc. NET JRF (AIR 21) GATE, MH-SET